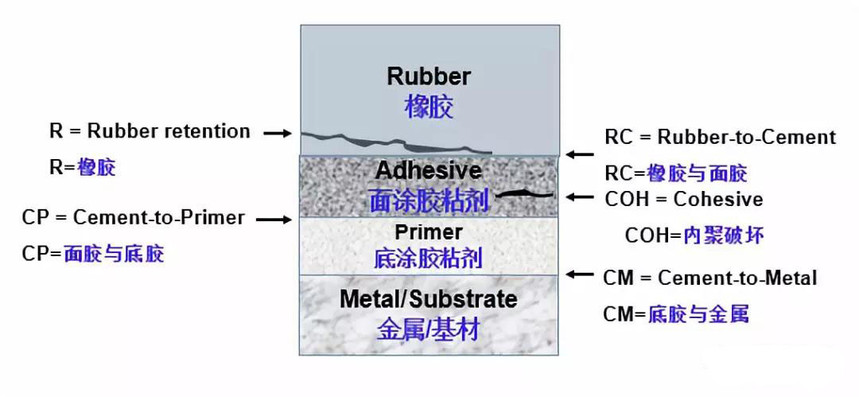
下面小编根据专业资料向大家介绍一下粘合的基础知识
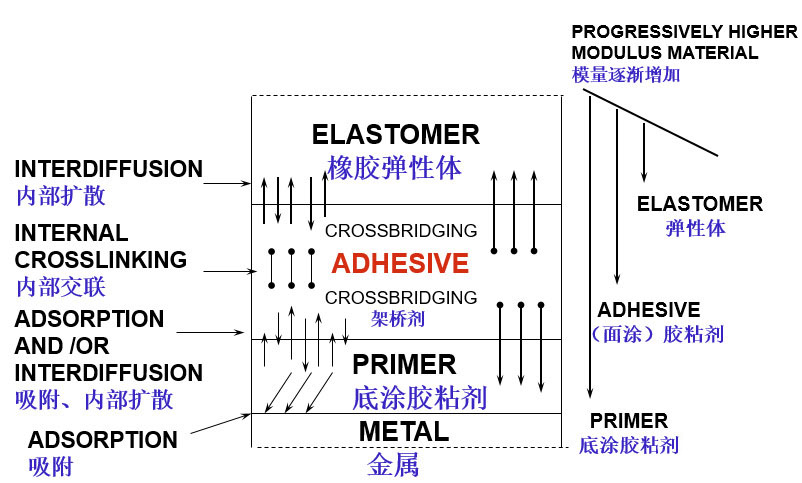
Mechanisms ofBonding:
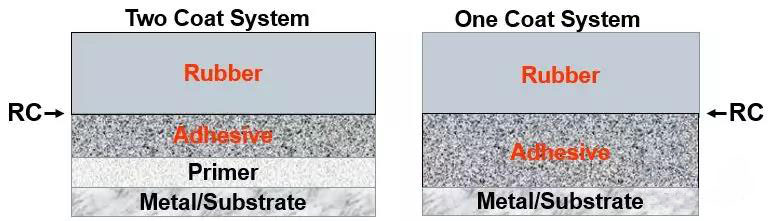
Two Coat System
双涂胶粘剂粘结机理
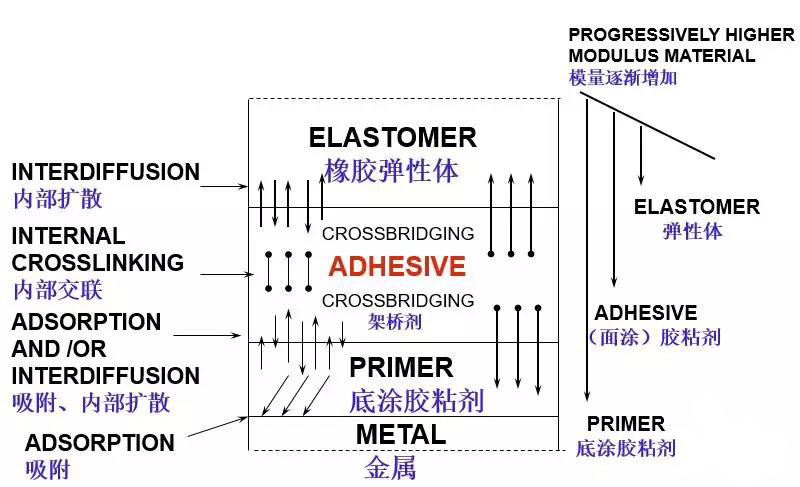
Mechanisms of Bonding:
One Coat System
单涂粘结机理
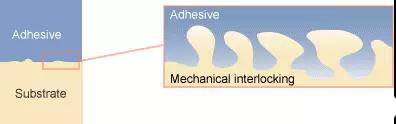
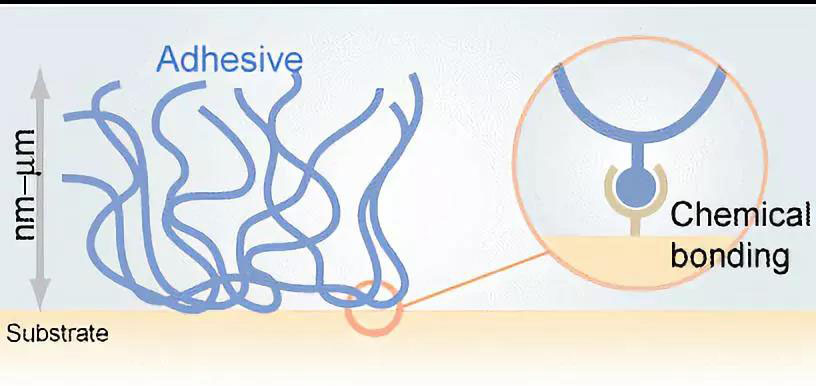
Mechanical and Chemical Mechanisms
物性及化学作用机理
Mechanical物性
Chemical化学
第二部分 粘结失效模式Bond Failure Modes
Methodsfor Troubleshooting Bond Failures
¨ Provide/definethe circumstances of the bond failure
定义粘结失效情况
¨ Inspect/determinefailure mode(s), location, amount
检测失效模式,位置,数量
¨ Reviewproduction materials and related processing
审核产品材料和相关工艺
¨ Create alist of potential causes
提出一系列潜在的因素
¨ Develop acorrective plan and test
提出改进的计划及测试
¨ Changematerial and/or process to verify cause(s)
根据影响因素更改材料或改进工艺
¨ Performonly one change at a time
每次只改变一个影响条件
BondFailure Modes of ASTM D429
ASTMD429定义的粘结失效模式
Cement-to-MetalFailure
CM失效模式
¨ Designatedas CM or M
CM或M的定义
¨ Primeror adhesive failure at the substrate interface
底涂或单涂胶粘剂与基材界面的粘结失效
¨ 25+%of failures in industry
在工业中占25%失效比例
¨ CommonCauses of Failure: Improper substrate preparation, improperhandling/application of Primer or Adhesive
典型的失效因素:不合适的基材处理,不正确的胶粘剂应用

Cement-to-Primer Failure
CP失效模式
¨ Designatedas CP
CP的定义
¨ Cement= Adhesive
Cement =面涂胶粘剂
¨ Failureoccurs between primer and adhesive
失效发生与底涂与面涂胶粘剂间
¨ <10%of failures in industry
工业上发生概率<10%
¨ CommonCauses of Failure: Contaminated primer surface or improper handling/applicationof Primer or Adhesive, plasticizer migration from compound
典型的失效因素:底涂表面被污染或不正确的胶粘剂应用,增塑剂的迁移

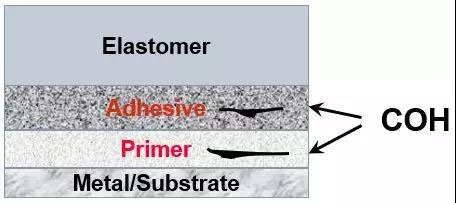
Cohesive Failure
胶粘剂内聚破坏
¨ Not aASTM type but failure occurs within either primer or adhesive layer
不是ASTM失效模式,但会在底涂或面涂胶粘剂层间发生
¨ Failureoccurs within either primer or adhesive layer
失效发生在胶粘剂的层间
¨ <5%of failures in industry
工业上发生概率<5%
¨ CommonCauses for Failure: Improper handling/application such as Primer or Adhesive istoo thick
典型的失效因素:不正确的胶粘剂应用或胶粘剂太厚
Rubber-to-CementFailure
RC失效模式
¨ Designatedas RC, cement = adhesive
RC失效定义,cement = 面涂胶粘剂
¨ Failureoccurs between rubber and adhesive
失效发生在橡胶与胶粘剂间
¨ Lookfor evidence of adhesive adhering to substrate, but not to rubber surface
胶粘剂与基材有良好的粘结,但是与橡胶表面粘结失效
¨ 50+%of failures in industry
工业上发生概率50+%
¨ CommonCauses of Failure: Adhesive applied too thin, improper mold cycle, bond-linestresses during de-mold, improper adhesive choice
典型的失效因素:胶粘剂太薄,不正确的硫化和脱模,胶粘剂选择错误
PartIII
ASTMD429 Bond Tests and Standards
ASTMD429粘结测试及标准
ASTMInternational
¨ ASTM isthe American Society for Testing and Materials
ASTM是美国对于测试及材料的标准
¨ Web site:www.astm.org
网址:www.astm.org
¨ CommitteeD-11 handles RTM bonding
D-11委员会执行RTM粘结
¨ ASTMmethods have been the standard for defining bond failure modes, lab andproduction testing and new product development for many years
ASTM已经成为定义粘结失效模式,实验室及产品测试,新产品开发的标准
¨ All testreport data reported with pull value and % rubber retention
所有的测试数据应记录拉伸强度和覆胶率

ASTM D429 Tests
ASTM D429 测试
¨ METHOD A: Button 扯离
¨ METHODB: Coupon 剥离
¨ METHODC: Conical 锥形扯离
¨ METHODD: Post Bond (PV bonding) 后硫化粘结测试
¨ METHODE: Rubber Lining 橡胶内衬测试
¨ METHODF: Buffer 弧面扯离
¨ METHOD G:Double Shear Cylindrical 双剪切测试
¨ METHOD H:Quadruple Shear 四面剪切测试
ASTMD429 Method B (Coupon)
¨ 45undefinedordm; or 90undefinedordm;peel, 2 inches (5 cm)/minute or 20 inches (50 cm)/minute, 45undefinedordm; peel preferreddue to shear angle
45undefinedordm; or 90undefinedordm;剥离,拉伸速度5CM或50CM每分钟,由于剪切角的原因, 45undefinedordm;剥离为首选
¨ Primaryand environmental tests
常规及耐环境测试
¨ Verydependent on tear and tensile strength of rubber
很大程度取决于橡胶的撕裂和拉伸强度
¨ Lowerdiscrimination than other test methods
相对于其他测试方法辨别力低
¨ Inexpensive,easy to coat and mold parts, quick feedback
便宜,方便涂胶和成型,快速反馈结果
¨ Compression,transfer and injection molding
模压,转移模,注塑成型
¨ Mostwidely used method for customer screening and our new product developments
广泛用于新产品开发和客户胶粘剂选型
ASTM429 Method C (Conical)
¨ Combination ofshear/tension
剪切/拉伸的结合
¨ Expensive inserts
标准件昂贵
¨ Time consuming,difficult to prepare and coat metal inserts
耗时久,表面处理及涂胶困难
¨ Good test for primeradhesion at the tip
对于顶端的底涂胶粘剂有良好的测试
¨ Transfer mold only
只用转移模成型
¨ Limited use due toexpense and time
由于费用及时间限制其使用
ASTM D429 Method D (Post Bond)
¨ Uses curedcompression set rubber
使用压缩变形放置橡胶
¨ Tensile test
拉伸测试
¨ Requires fixture jig(10% compression) to obtain bond-line pressure
需要固定夹套(10%压缩率)来得到粘结压力
¨ Compatible assemblyoil is used between adhesive and cured rubber
为方便装配可在胶粘剂和橡胶间使用专用装配油润滑
¨ Excellent, inexpensivetest for adhesion to cured rubber
对于硫化橡胶与胶粘剂是极好的,便宜的测试
ASTM D429 Method F (Buffer)
¨ Inexpensive tensiletest
便宜的拉伸实验
¨ Top surface isconvex, applies high shear force to primer at edges during pull test
在测试中表面的弧度给边缘的底涂胶粘剂以高的剪切力
¨ Good for primary orenvironmental tests
良好的常规或耐环境性测试
¨ Part can cycled infatigue testing (for example: 3 Hertz, 30% elongation for 1MM cycles)
零件可以在耐疲劳实验中循环使用(如:3Hz,30%延长率100万次疲劳实验)
¨ Transfer orinjection molding
转移模或注塑模成型
¨ *Preferred test ofmany Automotive applications
对于汽车应用零件是优选的测试方法
Part IV
Production Bond Test Methods
产品粘结测试方法
¨ Bondtests should be conducted per engineering specification for manufactured partsor customer’s special requirements:
测试应根据工程规范或客户特殊要求进行
¨ Fixturing for push or pull out or hand peel
推、拉、手工剥离应配备固定夹具
¨ Establish specification range: % rubber retention, 90%+is typical (plus load value from test machine), range depends upon material,bond surface area, type of force and speed of testing
确定规范:%橡胶保留,典型的附胶率为90+%(加上从测试仪器上得到的强度),规范的范围取决于材料,粘结表面,加载力的类型和测试速度
¨ Additional tests to include dynamic cycling, temperatureand fluid soaks, etc.
其他测试包括动态循环测试,高低温度和液体浸泡等
Production Bond Test Methods
¨ Establish bond test frequency: for example: 1 part permold cycle, 1 or 3 times per shift, etc.
确定粘接测试频率:如每模一个零件,每班次1-3个零件等
¨ Bond tests shouldcomplete separate the substrate from the rubber in the bonded region
测试应该将基材从的橡胶粘结区域完全分离开
¨ Most importantly,bond tests are a measurement of production quality and should prevent defectiveparts from reaching end customer
最重要的是,粘结测试是一种生产产品质量的检测方法,应防止有缺陷的产品流向最终客户
¨ Scrap rates aretypically maintained below 2%
典型的废品率应控制在<2%
¨ Periodic audits ofall processes are beneficial to ensure that processes are maintained withinproduction specifications
定期的对所有工艺的审核,将有利于工艺在产品生产规范中运行。















